安装软件
安装 python 2.7、pycharm、pip(python包管理工具)、django ( pip install django)
部署
pycharm 新建django工程
完成后,其目录如下:
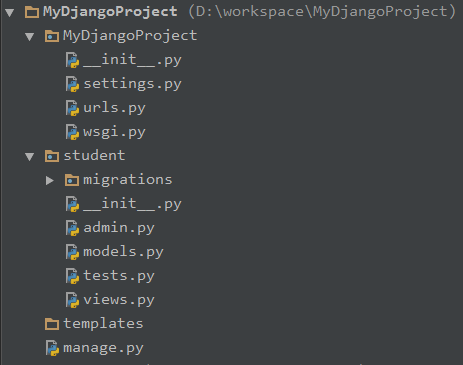
子目录mydjangoproject下表示工程的全局配置,分别为setttings.py、urls.py和wsgi.py,其中setttings.py包括了系统的数据库配置、应用配置和其他配置,urls.py则
表示web工程url映射的配置。
子目录student则是在该工程下创建的app,包含了models.py、tests.py和views.py等文件
templates目录则为模板文件的目录
manage.py是django提供的一个管理工具,可以同步数据库等等
启动
创建完成后,就可以正常启动了。点击run 按钮,启动时报错了:
traceback (most recent call last):
file “d:/workspace/mydjangoproject/manage.py”, line 10, in
execute_from_command_line(sys.argv)
file “d:\python27\lib\site-packages\django\core\management\__init__.py”, line 338, in execute_from_command_line
utility.execute()
file “d:\python27\lib\site-packages\django\core\management\__init__.py”, line 312, in execute
django.setup()
file “d:\python27\lib\site-packages\django\__init__.py”, line 18, in setup
apps.populate(settings.installed_apps)
file “d:\python27\lib\site-packages\django\apps\registry.py”, line 89, in populate
“duplicates: %s” % app_config.label)
django.core.exceptions.improperlyconfigured: application labels aren’t unique, duplicates: admin
应该是admin配置冲突了,打开setttings.py文件,发现admin配置重复了
installed_apps = (
‘django.contrib.admin’,
‘django.contrib.auth’,
‘django.contrib.contenttypes’,
‘django.contrib.sessions’,
‘django.contrib.messages’,
‘django.contrib.staticfiles’,
‘django.contrib.admin’,
‘student’,
)
注释掉其中一行后(为什么会有这个问题,估计是个bug),重新启动,ok
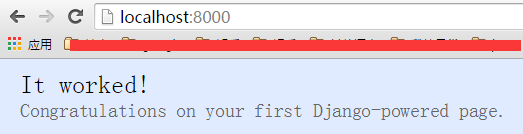
web工程添加页面
此时,我们尚没有写一行代码,程序就duang跑起来了! 快添加一个hello world的页面吧。
打开student/views.py文件,输入以下内容
def sayhello(request):
s = ‘hello world!’
current_time = datetime.datetime.now()
html = ‘ %s
%s
‘ % (s, current_time)
return httpresponse(html)
打开url.py文件,需要进行url映射的配置:
url(r’^student/’, sayhello)
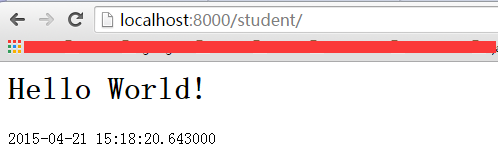
当用户输入http://**/student 时,便会调用sayhello方法,该方法通过httpresponse()将页面内容作为响应返回。
重启服务,访问http://localhost:8000/student/
在views.py页面可以将页面需要的元素通过字符串的形式,调用httpresponse()类作为响应返回到浏览器。但这样,页面逻辑和页面混合在一起,手写起来很繁琐,工作量比较大。如果我们需要展示一些动态的数据,而页面基本不改变的情况下,该怎么做呢?
比如在用户访问 http://localhost:8000/student/ 时,我们想动态展示一些学生的数据。可以这样做:
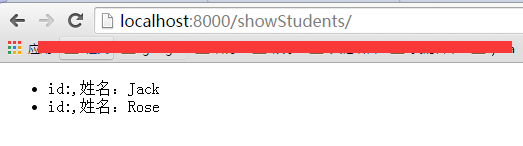
首先在templates目录下,新建 student.html文件,该文件作为模板,内容如下:
{% for student in students %}
id:{{ student.id }},姓名:{{ student.name }},age: {{ student.age }}
{% endfor %}
修改 views.py文件,添加方法showstudents()
def showstudents(request):
list = [{id: 1, ‘name’: ‘jack’}, {id: 2, ‘name’: ‘rose’}]
return render_to_response(‘student.html’,{‘students’: list})
该方法将list作为动态数据,通过render_to_response方法绑定到模板页面student.html上。
添加url映射,url(r’^showstudents/$’, showstudents)
修改settings.py模板配置:’dirs’: [base_dir+r’\templates’],
重启服务,访问http://localhost:8000/showstudents,出现:
至此,我们已可以正常将一些“动态”数据绑定到模板上了。但是怎么样访问数据库呢?
从数据库获取需要的数据,展示在页面上?
首先需要安装数据库驱动啦,即mysql_python,
接着配置数据库连接:
databases = {
‘default’: {
‘engine’: ‘django.db.backends.mysql’,
‘name’: ‘student’,
‘user’: ‘root’,
‘password’: ‘1234’,
‘host’: ‘127.0.0.1’,
‘port’: ‘3306’,
#’name’: os.path.join(base_dir, ‘db.sqlite3’),
}
}
配置完成之后,需要检测数据库配置是否正确,使用 manage.py shell命令,进入shell交互界面:
输入:
from django.db import connection
cursor = connection.cursor()
如果不报错,说明配置正确。
创建model,打开models.py,定义model如下:
class student(models.model)
id = models.bigintegerfield
name = models.charfield(max_length=20, default=’a’)
然后调用 manage.py syncdb
正常情况下,该步骤做完之后,model 会和数据库保持一致性。但是在测试中,命令执行成功后,却发现数据库并没有建立该表。
对于该种情况,做如下操作即可正常:
(1)注释掉models.py文件代码,执行 manage.py makemigerations student
【和manage.py migerate –fake】
(2)打开注释,执行【 manage.py makemigerations student和 】manage.py migerate命令
通过以上两步,便可正常操作了
views.py中添加方法:showrealstudents
def showrealstudents(request):
list = student.objects.all()
return render_to_response(‘student.html’, {‘students’: list})
urls.py添加映射 url(r’^showrealstudents/$’, showrealstudents)
重启服务,打开连接:http://localhost:8000/showrealstudents
页面输出正常。
至此,使用django,可以正常操作数据库,自定义模板,在页面展示数据了。
服务器
由于django自带轻量级的server,因此默认使用该server,但实际生产中是不允许这么干的,生产环境中通常使用apache httpd server结合mod_wsgi.so来做后端服务器。
以下部署环境为:python2.7.6
1、安装httpd-2.2.25-win32-x86-no_ssl.msi
2、将下载好的mod_wsgi.so 放在 d:\program files\apache software foundation\apache2.2\modules 模块下。
3、在新建的web工程 mydjangoproject目录下新建 django.wsgi文件
内容如下(相应的目录需要修改):
import os
import sys
djangopath = “d:/python27/lib/site-packages/django/bin”
if djangopath not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(djangopath)
projectpath = ‘d:/workspace/mydjangoproject’
if projectpath not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(projectpath)
apppath = ‘d:/workspace/mydjangoproject/mydjangoproject’
if apppath not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(apppath)
os.environ[‘django_settings_module’]=’mydjangoproject.settings’
from django.core.wsgi import get_wsgi_application
application = get_wsgi_application()
4、修改httpd.conf ,添加如下:
loadmodule wsgi_module modules/mod_wsgi.so
wsgiscriptalias / “d:/workspace/mydjangoproject/django.wsgi”
options followsymlinks
allowoverride none
order deny,allow
allow from all
ok,重启server,页面正常了。
在部署的过程中,遇到一个异常,如下:
the translation infrastructure cannot be initialized before the apps registry is ready
原因是django.wsgi一开始按照较为古老的写法,改为新版本的写法就ok了。