linux系统下调用动态库(.so)
1、linuxany.c代码如下:
#include “stdio.h”
void display(char* msg){
printf(“%s\n”,msg);
}
int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
2、编译c代码,最后生成python可执行的.so文件
(1)gcc -c linuxany.c,将生成一个linuxany.o文件
(2)gcc -shared linuxany.c -o linuxany.so,将生成一个linuxany.so文件
3、在python中调用
#!/usr/bin/python
from ctypes import *
import os
//参数为生成的.so文件所在的绝对路径
libtest = cdll.loadlibrary(os.getcwd() + ‘/linuxany.so’)
//直接用方法名进行调用
print
libtest.display(‘hello,i am linuxany.com’)
print libtest.add(2,2010)
4、运行结果
hello,i am linuxany.com
2012
windows下python调用dll
python中如果要调用dll,需要用到ctypes模块,在程序开头导入模块 import ctypes
由于调用约定的不同,python调用dll的方法也不同,主要有两种调用规则,即 cdecl和stdcal,还有其他的一些调用约定,关于他们的不同,可以查阅其他资料
先说 stdcal的调用方法:
方法一:
import ctypes
dll = ctypes.windll.loadlibrary( ‘test.dll’ )
方法二:
import ctypes
dll = ctypes.windll( ‘test.dll’ )
cdecl的调用方法:
1.
import ctypes
dll = ctypes.cdll.loadlibrary( ‘test.dll’ )
##注:一般在linux下为test.o文件,同样可以使用如下的方法:
## dll = ctypes.cdll.loadlibrary(‘test.o’)
2.
import ctypes
dll = ctypes.cdll( ‘test.dll’ )
看一个例子,首先编译一个dll
导出函数如下:
# define add_export q_decl_export
extern “c” add_export int addnum(int num1,int num2)
{
return num1+num2;
}
extern “c” add_export void get_path(char *path){
memcpy(path,”hello”,sizeof(“hello”));
}
这里使用的是cdecl
脚本如下:
dll=ctypes.cdll(“add.dll”)
add=dll.addnum
add.argtypes=[ctypes.c_int,ctypes.c_int] #参数类型
add.restypes=ctypes.c_int #返回值类型
print add(1,2)
get_path=dll.get_path
get_path.argtypes=[ctypes.c_char_p]
path=create_string_buffer(100)
get_path(path)
print path.value
结果如下:

我们看到两个结果,第一个是进行计算,第二个是带回一个参数。
当然我们还可以很方便的使用windows的dll,提供了很多接口
getsystemdirectory = windll.kernel32.getsystemdirectorya
buf = create_string_buffer(100)
getsystemdirectory(buf,100)
print buf.value
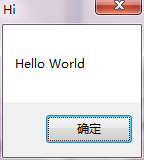
messagebox = windll.user32.messageboxw
messagebox(none, u”hello world”, u”hi”, 0)
运行结果如下: